
In Terrier 4.0, a new website search application was added to facilitate easy indexing and search of websites. This application combines the crawling functionality of Crawler4J, the Terrier's updatable Memory index structures and a Web-based Terrier front-end to demonstrate real-time indexing and retrieval of content from the Web. In particular, this application allows websites to be added dynamically to a frontier of pages to be crawled. Pages from the added websites will be downloaded in the background and indexed automatically. The browser-based search interface provides a basic search facility over the index produced.
The website search application is comprised of two main components. First, the org.terrier.services.websitesearch package contains a service class named WebsiteSearch that provides methods to crawl new websites, index documents from those websites, search over the index produced and write the index to disk. Second, a JSP (java servlet page) search interface is stored in src/webapps/websitesearch/ that provides search controls and rendering capability for the search results. The website search application is launched via the JSP search interface, which calls the java WebsiteSearch service internally top access all needed functionality.
Since the interface is represented as a java servlet page, it can be loaded into a Jetty webserver using http_terrier.sh by specifying the website search interface as follows:
bin/http_terrier.sh 8080 src/webapps/websitesearch/
This will host the website search demo at:
http://localhost:8080/
It is worth noting that the website search application configures itself automatically, regardless of the contents of the etc/terrier.properties file. It does this by overriding relevant variables in the WebsiteSearch and CrawlStrategy classes with reasonable defaults for Web search.
When first loaded, the splash screen will ask for you to enter a website to index, as shown below:
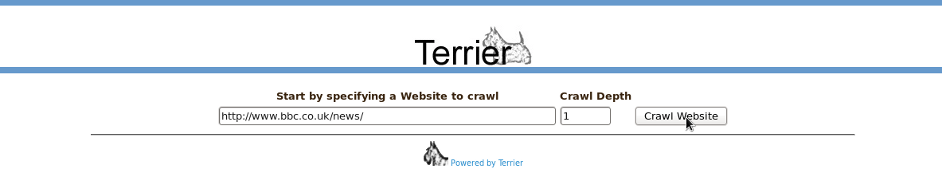
When the 'Crawl Website' button is clicked, the given hostname will be added to a crawl frontier (list of pages to crawl). A Web crawler will first download the page for that URL, and if it exists adds it to a MemoryIndex. Then any links on the page are added to the crawl frontier. The 'crawl depth' parameter specifies how many successive pages to follow the links from to find new documents. The crawler will restrict itself to crawling only pages from the originally named host, i.e. URL's that contain the hostname you originally entered.
Once crawling is underway, the main search interface will be loaded:
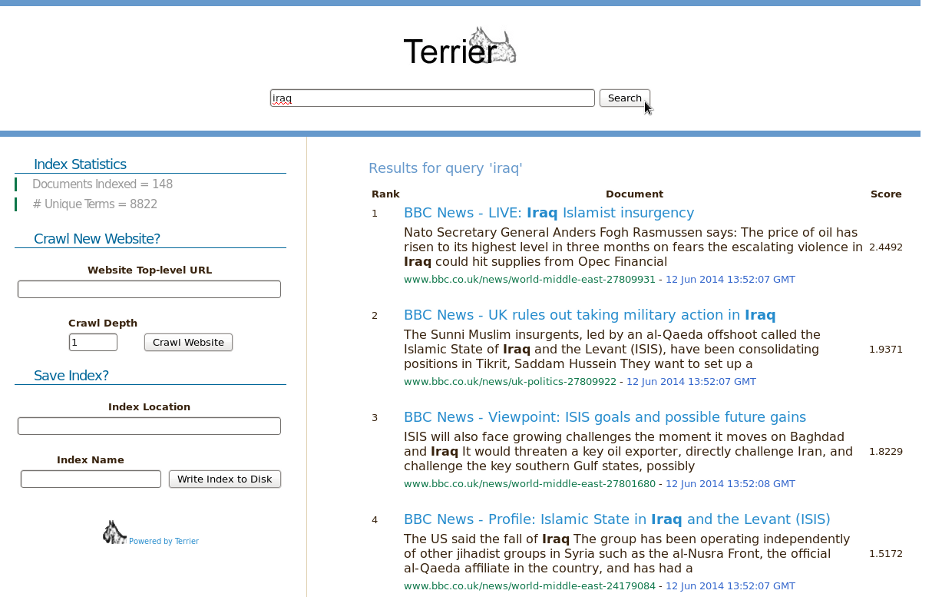
The top search bar facilitates retrieval over all documents crawled so far. The left sidebar provides statistics for the current index, allows new hosts to be added to the crawl frontier and for the current index to be saved as a classical Terrier on-disk index.
[Previous: Web-based Terrier] [Contents] [Next: TREC Experiment Examples]Copyright © 2015 University of Glasgow | All Rights Reserved